1. Flat-File Databases
When you first set up your database, you can choose to make a 'flat-file' database or a 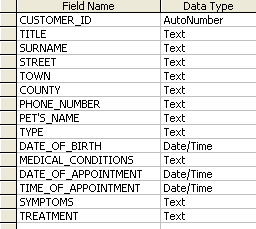 'relational' database (see next page).
'relational' database (see next page).
With a flat file database, all of your data is stored in one large table.
Take a database that a vet might use. In our example on the right, there is data about the owner of the pet i.e. name, address, phone number, there is data about the pet - name, type of animal, date of brith, and there is also data about any appointments the pet has.
This might seem pretty logical at first. But think about it, is it really as good as it seems? Every single time the pet has an appointment, the customer's title, surname, street, town, county, and phone number have to be entered. Also, the pet's name, type and d.o.b. also have to be entered. That would get fairly tedious having to enter so much data each time and there would be a great risk of making a mistake (Garbage In, Garbage Out - GIGO).
Repeating data unnecessarily like this is called 'data duplication'.
Challenge see if you can find out one extra fact on this topic that we haven't already told you
Click on this link: Flat File Database
