3. Writing efficient code
Computer programs are algorithms translated into code.
You can often translate the same algorithm into code in many different ways. And just like algorithms, some code is more efficient than others.
For example, part of an algorithm might involve iterating over an array. The pseudocode below does this:
list[2,4,5,2]
FOR p 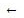 1 to LEN(list)
... do something
ENDFOR
1 to LEN(list)
... do something
ENDFOR
This seems fine, the variable p increments up to the length of the array. But notice that a function LEN is being called every time around the loop and this takes time.
A quicker way is to use a bit of extra memory to store the length in a variable and use that in the loop. Like this
list[2,4,5,2]
list_length 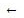 LEN(list)
FOR p
LEN(list)
FOR p 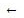 1 to list_length
... do something
ENDFOR
1 to list_length
... do something
ENDFOR
Now the LEN function is only called once. It is often the case that using extra memory improves time efficiency.
Challenge see if you can find out one extra fact on this topic that we haven't already told you
Click on this link: What is algorithm efficiency?
